Post without image !
Posts are the entries that display in reverse chronological order on your home page. In contrast to pages, posts usually have comments fields beneath them and are included in your site’s RSS feed.
To write a post:
- Log in to your WordPress Administration Panel (Dashboard).
- Click the Posts tab.
- Click the Add New Sub Tab
- Start filling in the blanks.
- As needed, select a category, add tags, and make other selections from the sections below the post. Each of these sections is explained below.
- When you are ready, click Publish.
Screen Options
The Screen Options allow you to choose which Post Fields are displayed, or not displayed, in the underlying SubPanel. Clicking on the Screen Options tab shows a list of the columns with a check-box next to each column. Check the box for each Post Field you want displayed, or uncheck the box to not display that module. Click the Screen Options tab again to close the Screen Options. These options are saved so that you can customize how your own editing screen looks.
Note: As of WordPress version 3.1, some screen options on the Post Administration Panel are hidden by default if they have not been saved before. Hidden by default: Excerpt, Post Author, Discussion, Custom Fields, Slug, Comments, Send Trackbacks, Revisions.
Descriptions of Post Fields
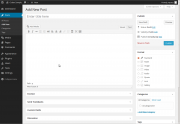
Title
- The title of your post. You can use any words or phrases. Avoid using the same title twice as that will cause problems. You can use commas, apostrophes, quotes, hypens/dashes, and other typical symbols in the post like “My Site – Here’s Lookin’ at You, Kid.” WordPress will clean it up for the link to the post, called the post-slug.
Post Editing Area
- The blank box where you enter your writing, links, links to images, and any information you want to display on your site. You can use either the Visual or the HTML view to compose your posts. For more on the HTML view, see the section below, Visual Versus HTML View.
Preview button
- Allows you to view the post before officially publishing it.
Publish box
- Contains buttons that control the state of your post. The main states are Published, Pending Review, and Draft. A Published status means the post has been published on your blog for all to see. Pending Review means the draft is waiting for review by an editor prior to publication. Draft means the post has not been published and remains a draft for you. If you select a specific publish status and click the update post or Publish button, that status is applied to the post. For example, to save a post in the Pending Reviewstatus, select Pending Review from the Publish Status drop-down box, and click Save As Pending. (You will see all posts organized by status by going to Posts > Edit). To schedule a post for publication on a future time or date, click “Edit” in the Publish area next to the words “Publish immediately”. You can also change the publish date to a date in the past to back-date posts. Change the settings to the desired time and date. You must also hit the “Publish” button when you have completed the post to publish at the desired time and date.
Publish box
- Visibility – This determines how your post appears to the world. Public posts will be visible by all website visitors once published. Password Protected posts are published to all, but visitors must know the password to view the post content. Private posts are visible only to you (and to other editors or admins within your site)
Permalink
- After you save your post, the Permalink below the title shows the potential URL for the post, as long as you have permalinksenabled. (To enable permalinks, go to Settings > Permalinks.) The URL is generated from your title. In previous versions of WordPress, this was referred to as the “page-slug.” The commas, quotes, apostrophes, and other non-HTML favorable characters are changed and a dash is put between each word. If your title is “My Site – Here’s Lookin’ at You, Kid”, it will be cleaned up to be “my-site-heres-lookin-at-you-kid” as the title. You can manually change this, maybe shortening it to “my-site-lookin-at-you-kid”.
Save
- Allows you to save your post as a draft / pending review rather than immediately publishing it. To return to your drafts later, visit Posts – Edit in the menu bar, then select your post from the list.
Publish
- Publishes your post on the site. You can edit the time when the post is published by clicking the Edit link above the Publish button and specifying the time you want the post to be published. By default, at the time the post is first auto-saved, that will be the date and time of the post within the database.
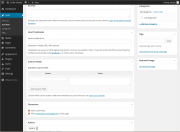
Post Tags
- Refers to micro-categories for your blog, similar to including index entries for a page. Posts with similar tags are linked together when a user clicks one of the tags. Tags have to be enabled with the right code in your theme for them to appear in your post. Add new tags to the post by typing the tag into the box and clicking “Add”.
Categories
- The general topic the post can be classified in. Generally, bloggers have 7-10 categories for their content. Readers can browse specific categories to see all posts in the category. To add a new category, click the +Add New Category link in this section. You can manage your categories by going to Posts > Categories.
Excerpt
- A summary or brief teaser of your posts featured on the front page of your site as well as on the category, archives, and search non-single post pages. Note that the Excerpt does not usually appear by default. It only appears in your post if you have changed the index.php template file to display the Excerpt instead of the full Content of a post. If so, WordPress will automatically use the first 55 words of your post as the Excerpt or up until the use of the More Quicktag mark. If you use an Explicit Excerpt, this will be used no matter what. For more information, see Excerpt.
Send Trackbacks
- A way to notify legacy blog systems that you’ve linked to them. If you link other WordPress blogs, they’ll be notified automatically using pingbacks. No other action is necessary. For those blogs that don’t recognize pingbacks, you can send a trackback to the blog by entering the website address(es) in this box, separating each one by a space. See Trackbacks and Pingbacks for more information.
Custom Fields
- Custom_Fields offer a way to add information to your site. In conjunction with extra code in your template files or plugins, Custom Fields can modify the way a post is displayed. These are primarily used by plugins, but you can manually edit that information in this section.
Discussion
- Options to enable interactivity and notification of your posts. This section hosts two check boxes: Allow Comments on this postand Allow trackbacks and pingbacks on this post. If Allowing Comments is unchecked, no one can post comments to this particular post. If Allowing Pings is unchecked, no one can post pingbacks or trackbacks to this particular post.
Password Protect This Post
- To password protect a post, click Edit next to Visibility in the Publish area to the top right, then click Password Protected, click Ok, and enter a password. Then click OK. Note – Editor and Admin users can see password protected or private posts in the edit view without knowing the password.
- Post Author
- A list of all blog authors you can select from to attribute as the post author. This section only shows if you have multiple users with authoring rights in your blog. To view your list of users, see Users tab on the far right. For more information, see Users and Authors.
Note: You can set basic options for writing, such as the size of the post box, how smiley tags are converted, and other details by going to Settings > Writing. See Writing Options SubPanel.